 Mark double boxes where
indicated.
Mark double boxes where
indicated.
1 through 10: Use Letters from Figure 1. Answers may be used more than once.
 Mark double boxes where
indicated.
Mark double boxes where
indicated.
1. Contains the cardiac center.
2. The somato-sensory area.
3. Origin of medial lemniscus fibers.
4. Terminus of third order neurons from spinothalamic tract.
5. Pre-central gyrus
6. Wernicke's area
7. Motor speech area
8. Center for coordination of all voluntary muscles
9. Area responsible for personality.
10. Pre-motor cortex (area for facilitation of skilled motor activities)
11 through 17: Use letters from Figure 2. Answers may be used more than once.
 Mark double boxes
where indicated.
Mark double boxes
where indicated.
11. The sensory relay center
12. The cerebellum
13. Membrane which covers the lateral ventricle
14. Brain area which controls the pituitary
15. Contains the auditory and visual reflex centers
16. Contains the center controlling respiratory rhythm.
17. Contains nuclei of nerves V, VI, VII.
18. The basal nuclei contains each of the following except:
(A) caudate nucleus, (B) lentiform nucleus, (C) thalamus, (D) corpus striatum.
19. Stereotyped muscular activities and motor responses to emotional stimuli are mediated by the:
(A) thalamus, (B) hypothalamus, (C) limbic system, (D) basal nuclei.
20. The cingulate gyrus, hippocampus, and mammillary body are all part of the:
(A) limbic system, (B) reticular formation, (C) brainstem, (D) cerebellum.
21. The center for emotional states and related behavior is:
(A) limbic system, (B) reticular formation, (C) brainstem, (D) cerebellum.
22. The center for personality:
(A) pre-motor area, (B) pre-frontal area, (C) pre-central gyrus, (D) thalamus.
23. The hypothalamus performs all but which of the following:
(A) controls and coordinates the autonomic nervous system,
(B) controls the endocrine system,
(C) body temperature regulation,
(D) hunger and thirst center,
(E) cognitive perception of touch, pressure, pain and temperature.
(A) trigeminal, (B) hypoglossal, (C) glossopharyngeal, (D) vestibulocochlear,
(E) trochlear.
24. Cranial nerve XII.
25. Innervates the superior oblique muscle.
26. Stimulates the muscles of chewing.
27. Innervates taste buds on the posterior portion of the tongue.
28. Carries senses of hearing and balance.
(A) choroid plexus, (B) superior colliculi, (C) arachnoid villi, (D) subarachnoid space,
(E) ventricles.
29. Location of absorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the venous sinus.
30. Derived from the original neural tube space (lumen inside the tube).
31. Contains cerebrospinal fluid lying just outside the pia mater.
32. Center for visual reflexes.
33. Source of cerebrospinal fluid.
In each of the following indicate if the characteristic describes:
(A) parasympathetic division, (B) sympathetic division, (C) both A and B,
(D) voluntary (somatic) nervous system.
34. Contains a single motor neuron between the CNS and the effector.
35. A system which can be activated in its entirety in response to stress.
36. Innervates virtually all vascular smooth muscle except in the genitalia.
37. Inhibits the salivary and gastrointestinal glands
38. Controls the heart under resting conditions.
39. Controls the muscles of respiration.
40. Stimulates release of glucose into blood by the liver.
41. CNS connection in the thoracic and lumbar portions of the spinal cord.
42. Principle post-ganglionic neurotransmitter is acetylcholine.
43. Has alpha and beta receptors.
44. Outflow via the pelvic splanchnic nerves.

45. Its muscle constricts to regulate the size of the pupil.
46. The aqueous humor:
47. Contains mostly cones:
48. The optic disk:
49. Absorbs the aqueous humor:
50. The conjunctiva:
51. The region of greatest visual acuity (sharpness) is the:
(A) optic disk, (B) fovea centralis, (C) optic chiasma, (D) rods.
52. The principal function of cones is: (A) vision in dim light, (B) vision in bright light,
(C) color vision, (D) A and C, (E) B and C.
53. What is the main function of rods in the eye?
(A) depth perception, (B) color vision, (C) vision in dim light,
(D) accommodation for near vision, (E) both A and C.
54. Glaucoma is due to abnormally high pressure in the:
(A) aqueous humor, (B) vitreous humor, (C) semicircular canals, (D) ampulla.
55. The cells of the retina in which action potentials are generated are the:
(A) rods and cones, (B) bipolar cells, (C) ganglion cells, (D) amacrine cells.
56. Receptors for static equilibrium are located in the:
(A) semicircular canals, (B) cochlear duct, (C) organ of Corti, (D) saccule and utricle.
57. The reason why the cornea can be transplanted without rejection is because the cornea:
(A) is not a living tissue, (B) has no nerve supply, (C) has no blood supply,
(D) does not contain connective tissue.
58. The oval window is connected to:
(A) vestibular canal (scala vestibuli), (B) tympanic canal (scala tympani),
(C) external auditory meatus, (D) organ of Corti.
59. The sense organ for hearing is the:
(A) semicircular canals, (B) cochlear duct, (C) organ of Corti, (D) saccule and utricle.
60. The first stop in the visual pathway from the eye, after the optic chiasma, is the:
(A) superior colliculi, (B) lateral geniculate body of the thalamus,
(C) the visual cortex, (D) the temporal lobe.
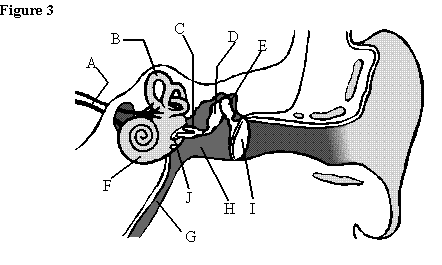
61 through 65
Apply to Figure 4
61. The oval window
62. The cochlea
63. The stapes
64. Eustachian canal
65. The tympanic
membrane
Answers
| 1 J | 11 J | 21 A | 31 D | 41 B | 51 B | 61 J |
| 2 E | 12 F | 22 B | 32 B | 42 A | 52 E | 62 F |
| 3 J | 13 A | 23 E | 33 A | 43 B | 53 C | 63 C |
| 4 E | 14 I | 24 B | 34 D | 44 A | 54 A | 64 G |
| 5 C | 15 E | 25 E | 35 B | 45 H | 55 C | 65 I |
| 6 H | 16 G | 26 A | 36 B | 46 M | 56 D | |
| 7 O | 17 H | 27 C | 37 B | 47 I | 57 C | |
| 8 I | 18 C | 28 D | 38 A | 48 K | 58 A | |
| 9 N | 19 D | 29 C | 39 D | 49 N | 59 C | |
| 10 B | 20 A | 30 E | 40 B | 50 D | 60 B |